When a client’s spouse dies, the client is likely overwhelmed. In addition to grieving the loss of their life partner, they face a seemingly endless list of tasks that must be completed.
So, it comes as a relief when the client hears from their CPA, probate attorney or other advisor that no federal estate tax return is required by the tax laws to be filed for the deceased spouse. Strike it off the list and move on!
However, the client’s tax practitioner must be alert to the fact that, just because a federal estate tax return is not compulsory under the tax laws, it does not necessarily mean that one should not be filed anyway.
In some cases where filing is not mandatory, it is appropriate to file a federal estate tax return to transfer the deceased spouse’s unused federal estate tax exclusion to the surviving spouse.
When filing an estate tax return is not mandatory under the tax laws, the filing decision depends on a simple formula. First, find out the date the surviving spouse plans to die. Second, compute what the combined value of the surviving spouse’s estate and taxable lifetime gifts will be on that date. Third, determine what the federal estate tax exemption will be on that date.
If the surviving spouse intends to die on a date when the federal estate tax exemption exceeds the combined value of the surviving spouse’s estate and taxable lifetime gifts, there is no need to file an estate tax return for the deceased spouse. If the surviving spouse plans to die on a date when the federal estate tax exemption is below the combined value of the surviving spouse’s estate and taxable lifetime gifts, an estate tax return should be filed for the deceased spouse so that the deceased spouse’s unused federal estate tax exclusion can be transferred to the surviving spouse.
The implausible scenario in the previous paragraph was prompted by the author’s conversations with surviving spouses and their advisors in which they have lamented that the portability decision would be easier if at least one of the three variables in the formula could be predicted. However, the fundamental formula in the scenario is valid, and the author’s goal is to encourage tax practitioners to consider this formula when counseling a surviving spouse and examine whether an estate tax return should be filed for the deceased spouse, even when not required by law.
Filing Not Required if Under Exclusion
Generally, filing a federal estate tax return (Form 706) for a deceased person (“decedent”) is not required by law if the combined value of the decedent’s gross estate and taxable lifetime gifts is below the decedent’s basic exclusion amount. The basic exclusion amount is $12.06 million for decedents dying in 2022, $12.92 million for decedents dying in 2023 and $13.61 million for decedents dying in 2024. A comprehensive discussion of all of the items that constitute the gross estate and taxable lifetime gifts is outside the scope of this article.
Filing Required to Transfer Deceased Spouse’s Unused Exclusion to Surviving Spouse
When a person dies, the person’s federal estate tax basic exclusion amount (i.e., the exclusion in effect for the year of death) is applied against the combined value of the person’s taxable estate and taxable lifetime gifts. If the combined value of the taxable estate and lifetime gifts is below the person’s exclusion, not all of the person’s exclusion will be used and there will be some exclusion remaining. If the person was not married at the time of death, any remaining exclusion is lost and cannot be used by anyone else.
However, if the person was married at the time of death, the remaining exclusion (commonly referred to as the deceased spousal unused exclusion amount, or “DSUE” amount) can be transferred to the person’s surviving spouse. This concept of transferring the deceased spouse’s unused exclusion to the surviving spouse is called “portability.”
The opportunity to transfer the DSUE amount to the surviving spouse is available only if appropriate action is taken in a timely manner. Electing portability on a timely-filed Form 706 is currently the only way for the decedent’s unused exclusion to be transferred to the decedent’s surviving spouse. Practitioners should compare the estimated combined value of the surviving spouse’s taxable estate and taxable lifetime gifts to the range of federal estate exemption levels that may apply to the surviving spouse in the future to determine whether it is advisable to seize this opportunity.
Valuable Opportunity to Reduce or Eliminate Gift and Estate Tax
Portability adds the decedent’s unused federal estate tax exclusion amount to the decedent’s surviving spouse’s own basic exclusion amount that is already available to the surviving spouse for both federal gift and estate tax purposes.
When the portability election has been made on a timely-filed Form 706, the surviving spouse can then use the
DSUE amount against the surviving spouse’s lifetime gifts and when the surviving spouse dies, the personal representative of the surviving spouse’s estate can apply the DSUE amount against the surviving spouse’s taxable estate – all in addition to the surviving spouse’s own basic exclusion amount, which remains fully available for use against the surviving spouse’s lifetime gifts and estate at death.
Current High Exemption Sunsets on December 31, 2025
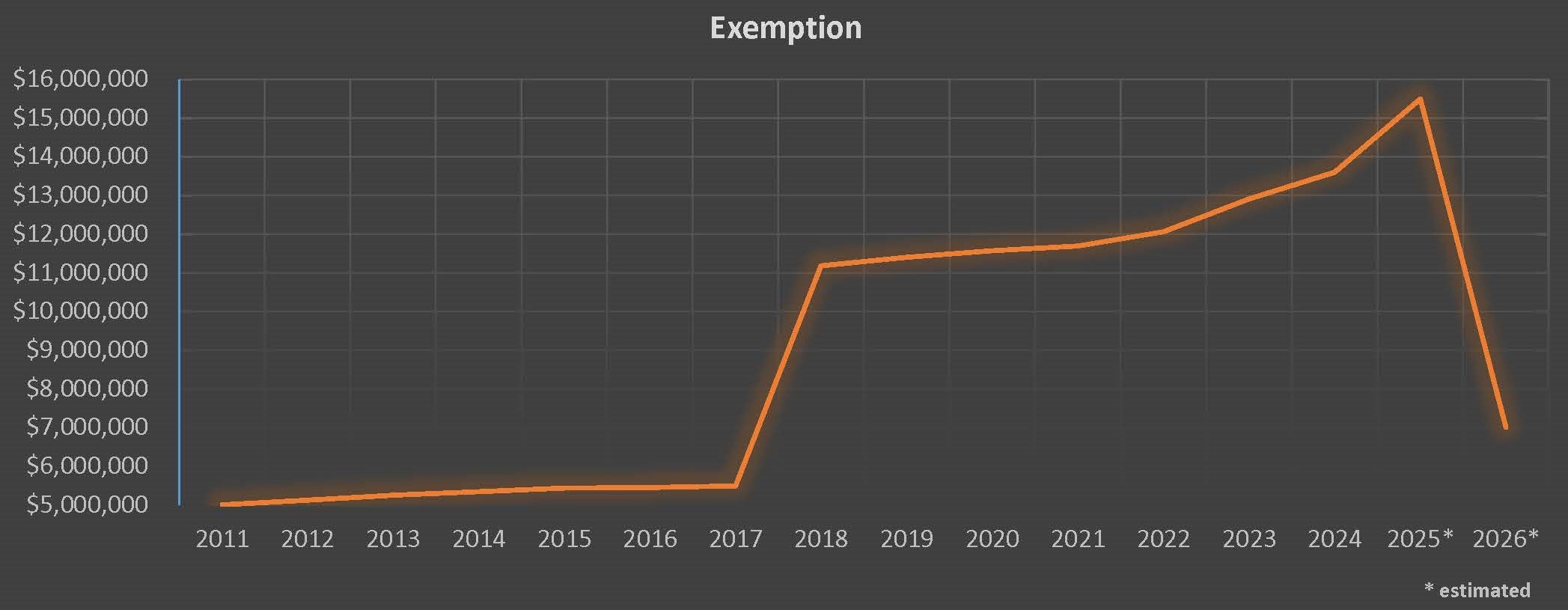
Keep in mind that, while the federal gift and estate tax exclusion available to a person today is 10 million dollars, adjusted for inflation ($13.61 million in 2024), the law that established the current historically high exclusion levels expires (“sunsets”) December 31, 2025.
On January 1, 2026, the per-person exclusion amount drops to five million dollars, adjusted for inflation. Therefore, the tax practitioner should keep this “sunsetting” of the current high exemption levels in mind when helping the client to decide whether to file an estate tax return for the client’s deceased spouse.
Surviving Spouse Has Significant Assets or Has Made Significant Lifetime Gifts
Arguably, filing an estate tax return to elect portability is essential when the combined value of the surviving spouse’s assets (including assets that the surviving spouse receives as a result of the death of the deceased spouse) and taxable lifetime gifts exceeds the current exemption ($13.61 million in 2024). If an estate tax return is not filed now for the deceased spouse, the chances are high that estate tax will be due at the death of the surviving spouse (to the tune of 40% of the amount that the combined value of the surviving spouse’s taxable estate and taxable lifetime gifts exceeds the exemption in effect on the date of the surviving spouse’s death).
Filing an estate tax return to elect portability should be seriously considered when the combined value of the surviving spouse’s assets (remembering to include assets that the surviving spouse receives as a result of the death of the deceased spouse) and taxable lifetime gifts is near the current exemption ($13.61 million in 2024), because the DSUE amount may be needed to offset any growth in the value of the surviving spouse’s assets that outpaces any future increases in the estate tax exemption.
Or, as discussed in the next section, the DSUE amount might be needed to supplement the surviving spouse’s own basic exclusion amount if the surviving spouse dies after December 31, 2025, and Congress does nothing to extend the current high exemption levels.
If an estate tax return is not filed now for the deceased spouse, estate tax could be due at the death of the surviving spouse (40% of the excess of the surviving spouse’s taxable estate and lifetime gifts over the exemption in effect on the date of the surviving spouse’s death).
Surviving Spouse Has Moderate Assets – Exemption Plummets in the Future
Given that under current law the federal gift and estate tax exemption is scheduled to drop to $5 million (indexed for inflation) in 2026, filing an estate tax return to elect portability may be appropriate even when the combined value of the surviving spouse’s assets (including assets that the surviving spouse receives as a result of the death of the deceased spouse) and taxable lifetime gifts is well under the current exemption amount.
Consider the following hypothetical. A married decedent dies in 2023, when the exemption is $12.92 million. The value of the decedent’s estate is $5 million and the value of the surviving spouse’s estate is $3 million. The decedent’s entire estate passes to the surviving spouse.
An estate tax return is not mandatory under federal tax law. After inheriting $5 million from the deceased spouse, the value of the surviving spouse’s estate is now $8 million. The surviving spouse dies in 2026 when the exemption is $7 million. If no estate tax return was filed for the spouse who died in 2023, there may be estate tax of $400,000 owed at the death of the surviving spouse in 2026 ($8 million estate – surviving spouse’s $7 million basic exclusion amount = $1 million taxable estate x 40% = $400,000).
In contrast, if an estate tax return had been filed for the spouse who died in 2023, there is no estate tax owed when the surviving spouse dies in 2026 because the DSUE amount of $12.92 million transferred from the spouse who died in 2023 to the surviving spouse, plus the surviving spouse’s own $7 million basic exclusion amount, will be applied to the surviving spouse’s $8 million estate. So, in this hypothetical, filing an estate tax return for the spouse who died in 2023, even though not required by law, would save $400,000 in estate tax.
Imagine if the reason the estate tax return was not filed in this hypothetical was because the tax practitioner had not made the client aware of the concept of portability! Please see the following graph for fluctuations of the estate tax exemption.
Reasons Clients May Decline to File for Portability
There could be one or more downsides to filing an estate tax return for portability. The cost of having an estate tax return prepared and the uncertainty of future circumstances (e.g., multiple unknown variables such as the value of assets remaining at the surviving spouse’s death and what the exemption will be at the surviving spouse’s death) may be the most common factors that discourage filing. Similarly, the time commitment, effort and cost involved in gathering information and documents and engaging appraisers and business valuation experts may tip the scales against filing.
One point to consider when making the filing decision is that, when the portability election is made, the IRS is allowed to examine the return after the relevant limitation periods have expired for the restricted purpose of making determinations with respect to the DSUE amount. This may or may not be a deterrent to filing.
Another consideration is that a surviving spouse is limited to using the DSUE amount of the last deceased spouse, so in the narrow set of facts where the surviving spouse files an estate tax return to elect portability of their deceased spouse’s unused exclusion, marries a new spouse and then is predeceased by that new spouse, it would be possible for the surviving spouse to lose all or a portion of the benefit of portability of the first deceased spouse’s unused exclusion. This remote possibility of losing the benefit of portability may be a dissuading factor in the filing decision.
Simplified Rules for Portability-only Returns
One facet that may swing the pendulum toward filing a portability return is the relaxed rules that are available for returns that are filed solely to elect portability.
Relaxed Valuation Method. When an estate tax return is filed for the purpose of electing portability, the value of certain property that qualifies for the marital or charitable deduction can be estimated on the return. In such a case, no formal appraisals or formal valuation reports are needed to support the estimated values for those assets.
Extended Filing Deadline. Generally, an estate tax return is due within nine months after the date of the decedent’s death or within 15 months with a timely-filed extension. A special five-year extension is available for filing an estate tax return to elect portability for an estate that is not otherwise required to file an estate tax return. This relief enacted by the IRS in July of 2022 came as welcome news to tax practitioners, surviving spouses and other interested parties (likely including a number of professional liability insurance carriers!).
If no estate tax return is required to be filed, this special extension may be obtained by filing Form 706 on or before the fifth anniversary of the decedent’s death and stating at the top of the return that it is “Filed Pursuant to Rev. Proc. Documenting the Discussion With the Client
When factors indicate that electing portability may be beneficial, the tax practitioner should discuss the general advantages and disadvantages of filing with the client (or refer the client to a practitioner who is qualified to provide such advice to the client).
It is recommended for the tax practitioner to be in communication with the probate attorney representing the executor of the decedent’s estate. Often the surviving spouse serves as the executor of the deceased spouse’s estate, which can simplify the communication and decision-making process.
The goal is to explain the general concepts, advantages and disadvantages of filing a portability return to the client and recommend collaboration with the probate attorney, the decedent’s and surviving spouse’s financial advisor(s) and other professionals to assist with gathering the specific details required to make an informed decision on filing.
The tax practitioner should document the portability discussion and the client’s decision on whether to file. The practitioner may wish to provide a letter to the client summarizing their discussion on the advantages, disadvantages, deadline, etc. relating to filing a portability return and request for the client to return a signed copy of the letter with the client’s filing decision noted on the letter.
Taking a Closer Look at Utilizing Portability
Following the death of a spouse, the surviving spouse is likely not immediately concerned about minimizing future federal transfer tax liability, especially in light of today’s relativity high exemption. However, absent legislative action, significant changes are in store for transfer tax laws when the current law sunsets on December 31, 2025.
The surviving spouse may not realize that there is action that can be taken now to increase the reserve of exclusion that can be used to minimize or eliminate gift and estate tax liability many years down the road. When appropriate, the tax practitioner should encourage the client to take a closer look at utilizing portability of the client’s deceased spouse’s unused exclusion.

About the Author: Nikki L. Laing, CPA, JD, is a member of the law firm of Godwin Laing, PLLC, located in Texarkana, Texas. She may be contacted at nlaing@godwinlaing.com.
Please see the pdf file of this article for footnotes.



















