Blockchain: The Architecture Underlying Crypto Assets
By Josef Rashty, CPA
The use of cryptocurrencies has been expanding rapidly and many more companies accept them in their ordinary course of business. The underlying technology of cryptocurrencies and digital assets is “blockchain” or distributed ledger.
The distributed ledger based on blockchain is unlike a traditional network since it does not have a common central authority. Blockchain consists of a network of interlinked computers that no single person can control or manipulate.
Bitcoin was the first and is probably the most popularly used cryptocurrency. An anonymous software developer known by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto introduced it during the 2008 global financial crisis for companies and individuals to buy goods, services and currencies online.
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. (An immutable ledger means that participants cannot change or tamper with recorded transactions in a shared ledger.) If a recorded transaction has an error, a new transaction should reverse the error, with both transactions being visible.
An asset can be tangible (e.g., a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (e.g., intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). If all participants on the database do not validate a particular transaction, that transaction will not get accepted. This feature of blockchain reduces the risk and cuts the costs for all involved.
This article is a brief explicative summary of the underlying technology of crypto assets. It is not a technical reference and aims at an audience with a business background. Today’s CPA in its May/June 2022 issue published an article by Josef Rashty, “ Accounting and Tax Implications of Crypto Assets.” The following article discusses the underlying technical architecture of the crypto assets and is the continuation of the earlier publication.
Blockchain technology is complicated and overwhelming even for technology savvy individuals; thus, for the reasons of brevity, this article has focused on expounding on only a few important and relevant concepts.
Blockchain Technology
A blockchain is a distributed, peer-to-peer database that hosts a continuously growing number of transactions. Each transaction is a “block” and is secured through cryptography, time-stamped, and validated by all authorized members of the database using consensus algorithms.
Each block connects to the ones before and after it. These blocks form a data chain as an asset moves from place to place or ownership changes hands (see Figure 1). The blocks confirm the exact time and sequence of transactions, and the blocks link securely together to prevent any block from being altered or a new block inserted between two existing blocks.
There is a misconception that only one universal blockchain exists, but each cryptocurrency has its blockchain – for example, bitcoin and ethereum use different blockchains. There are other public blockchains, in addition to bitcoin and ethereum, and private blockchains that provide access to a limited group of parties.
Traditional Network Technologies
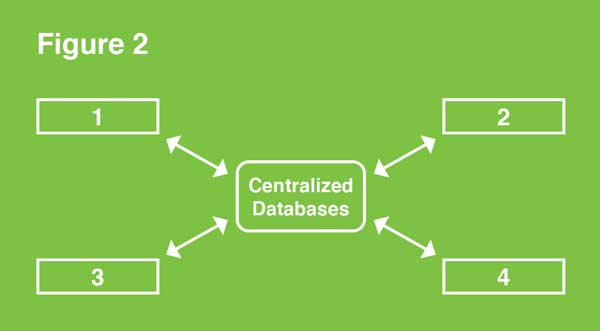
The traditional network structure requires a central authority with decision-making power and this central authority manages all aspects of the environment. This feature does not make this type of network necessarily ineffective or outdated.
Certain business functions work well in such environments, but they have challenges. The challenges include:
- It takes significant time and costs to process transactions and manage the network.
- It cannot validate the participating transactions.
- It is subject to error and vulnerable to hacking.
Figure 2 depicts the participating transactions and the central power and authority of the traditional network.
In a decentralized database, no one person or company controls the database. Instead, the database is spread across multiple sources to create a shared database.
Distributed Ledger Technologies
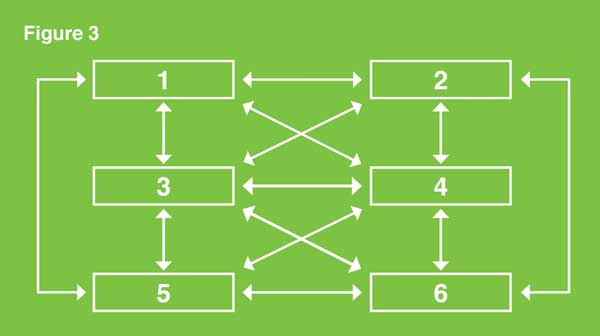
Rules, rather than a central authority, control the distributed ledger technologies. All members can access the network and have a consensus to add transactions to the database. Each transaction is encrypted using an algorithm and a “key” to convert an unencrypted input into an encrypted output.
The distributed ledger technology underlying private blockchains (discussed later in this article) appeals to large corporations. These private chains allow for a more traditional frame of control since they can grant rights and restrictions to participants in a closed and controlled network.
Thus, transactions in a distributed ledger have the following characteristics:
- Transactions are processed quickly and at a lower cost since distributed ledgers have a set of rules on the blockchain to speed up the processing of transactions (smart contracts, which is a set of rules stored on a blockchain to speed up the execution of transactions automatically).
- Since all participants validate the transactions, they are less prone to error and more secure.
- Participants cannot change or tamper with transactions when they record them in the shared ledger.
Figure 3 depicts the participating transactions in a distributed ledger network.
Types of Blockchain
There are four main types of blockchain networks.
- Decentralized public blockchains allow anyone to join them. They give equal rights of access to participants to all the nodes. The participants have equal rights, create new blocks of data and validate blocks of data.
- A centralized power permits participants to join a private network and determines who can be a node. The central authority also does not necessarily grant each node equal rights to perform its functions. Thus, private blockchains are only partially decentralized because access to them is restricted.
- Consortium blockchains require permission to access and a group of organizations, rather than one entity, governs them, as in the case of the private blockchain. It has private and public features. A consortium blockchain is private, with limited access to a particular group and eliminates the risks that just one entity can control the network in a private blockchain.
- A single organization controls a hybrid blockchain, but a level of oversight exists for some transaction validations. A hybrid is a mix of private and public. It gives organizations better control over what they want to achieve rather than change their plans on the limitation of the private and public technology. An example of a hybrid blockchain is IBM Food Trust, which improves efficiency throughout the whole food supply chain.
Security
Blockchain technology has a data structure with inherent security qualities. The principles of cryptography, decentralization and consensus ensure trust in transactions. This architecture makes blockchain immutable and provides for a self-validating audit trail.
In most blockchains or distributed ledger technologies, the data consists of blocks, and each block contains a transaction or bundle of transactions. Each new block connects to the blocks before it in the cryptographic chain and architecture makes it nearly impossible to tamper with the transaction. An agreed-upon consensus mechanism, which secures the correctness and validity of the database, controls the integrity and security of transactions.
This architecture ensures that once a transaction is validated and input into the system, it can never be deleted, edited or changed. Although they have shown relative resiliency to outside attacks, there is no total immutability – blockchain technology produces a tamper-proof ledger of transactions, but this is not to say that it is immune to cyberattacks and fraud.
Blockchains are not fully resilient to cyber-attacks and do not have total immutability. Thus, it is feasible to manipulate the known vulnerabilities in the infrastructure. For example, fraudsters may steal the access keys and conduct fraudulent activities on behalf of the rightful owners – a private key is analogous to a password associated with cryptocurrency. Computer hackers may also compromise the system and conduct fraudulent transactions.
A problem that blockchain cannot resolve is collusion – a traditional fraud scheme by two employees colluding to reverse or manipulate blocks of transactions. Reports of fraudulent activities and hacking of blockchains have become sensual events, and media report them with commotion and fanfare almost daily.
Ransomware, with unknown origins, has often attacked and hacked blockchains. Ransomware attacks could involve both state and non-state players. The U.S. government has expressed concerns about the illegal use of cryptocurrencies in perpetuating these attacks and is taking steps to counter them.
Blockchain and Accounting Systems
Blockchains can support accounting systems that require transaction verification from a neutral third party. A “triple party” accounting information system is created, consisting of two parties involved in the transaction and the intermediary. In a distributed shared ledger, participants record transactions only once by eliminating the duplication of effort typical of traditional business networks.
For example, each account in the double-entry system will have a corresponding blockchain account. When a company makes a payment to one of its accounts payable vendors, the system creates a journal entry debiting accounts payable and crediting cash in the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. Then, it makes a corresponding entry simultaneously to the blockchain account and ledger using a token. The token executes a payment upon certain conditions (e.g., due date).
Businesses rely on accurate and timely information. The faster they receive more precise information, the better. Blockchain is ideal for delivering that information because it provides immediate and transparent information stored on an immutable ledger that only members who have permission can access. The network can track orders, payments, accounts, production and more. Since all members share a single view of data, they can see all details of a transaction end to end.
While the technology may appear to have promising implications in accounting, it is at an infancy stage and there are challenges to fully adopting it. These challenges are:
- Technological requirements,
- Training of employees, and
- Privacy concerns.
Crypto Assets
Companies are increasingly using crypto assets for their payments, receipts or investments, and they rely on the capabilities of blockchains to execute these processes. We have had scant guidance from accounting literature dealing with digital assets and their operating technological environment.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plan to address cryptocurrencies more comprehensively. They plan to issue more specific guidance to provide a substratum to deal with the particular and emerging accounting issues of digital assets.
The recent volatility of crypto assets has made the need for new guidance even more pressing. For example, bitcoin fell below $17,700 in mid-June. Tesla announced that it recorded a $170 million impairment charge against the $1.5 billion worth of its bitcoin holdings for the first six months of 2022 (The WSJ, July 26, 2022). MicroStrategy, which currently owns roughly $3.1 billion bitcoins, announced a loss of $1 billion, much of that from devaluation of its bitcoin holdings (The WSJ, August 4, 2022).
Following is a summary of recent accounting guidance on digital assets.
In December 2019, the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) issued its nonauthoritative practice aid, Accounting for and Auditing of Digital Assets. The consensus from the AICPA practice aid is that companies should classify crypto assets, based on Topic 350, on their balance sheets as indefinite-lived intangible assets. (Generally, intangible assets lack physical substance.)
In March 2022, the SEC staff issued Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) 121, which outlines the staff’s views on how public entities should account for obligations to safeguard the cryptocurrencies of third parties. This SAB does not apply to entities that own and maintain their control over those digital assets themselves.
In May 2022, FASB added a project to its technical agenda to improve the accounting for, and disclosure of, certain digital assets.
In September 2022, FASB discussed the scope criteria for the project. FASB decided that crypto assets that are held by an entity must meet the following criteria to be within the project’s scope:
- Meet the definition of intangible asset as defined in the Codification Master Glossary;
- Do not provide the asset holder with enforceable rights to, or claims on, underlying goods, services or other assets;
- Are created or reside on a distributed ledger or “blockchain;”
- Are secured through cryptography; and
- Are fungible.
FASB also discussed the different entity types that would be within the scope of the guidance. It decided that all entities would be within the scope of the project and that throughout the remaining deliberations, FASB will consider the applicability of its decisions to those entities.
Summary
Blockchain technology is a database that allows data to be stored and exchanged on a peer-to-peer basis. The adoption and acceptance of blockchain technology have grown steadily since its introduction as a platform for cryptocurrency transactions.
Businesses now use this technology to manage their supply chains, verify payments, create algorithm-based contracts and many other functions. The blockchains in business enterprises are usually private or permission based that grant rights only to certain parties to read and write transactions.
In distributed ledger technology, all parties on the blockchain control and maintain information. This mechanism provides an additional layer of system control. However, this does not imply that the technology is immutable – it has been subject to hacking and cyberattacks almost daily.
After being hands-off toward cryptocurrencies, it appears that finally, regulators in Washington, D.C. plan to build a regulatory framework governing the industry and its use. FASB and the SEC have focused on cryptocurrencies recently and have initiated several projects to address the related accounting and reporting issues.
SEC Chairman, Gary Gensler, has likened cryptocurrency markets to the Wild West and wants to maintain tight controls over their use and operations. The SEC monitors bitcoins and other cryptocurrency developments and transactions regularly.
For example, asset managers for years have been trying to sell bitcoin Electronic Exchange Funds (ETFs) – existing ETFs only deal with futures.
In a dramatic move, in July 2022, an investment firm made a bid to change its large bitcoin fund into an ETF. The SEC rejected this bid, which reflects that the SEC is tightening its grip both on cryptocurrency transactions and operations (The WSJ, July 1, 2022).
About the Author: Josef Rashty, CPA, Ph.D. (Candidate), is a member of the Texas Society of CPAs and provides consulting services in Silicon Valley, Calif. He can be reached for comments and suggestions at j_rashty@yahoo.com.

















